In mathematics, we encounter various shapes and figures that play a significant role in our understanding of the world around us. One such figure is the cube. This article will explore the mathematical concept of a cube, answering questions like “What is a cube in math?”, “How many edges does a cube have?”, “How many sides does a cube have?”, and “How many vertices does a cube have?”.
Differentiated Topics: Square and Cube
The most significant difference between the square and cube is the fact that the square is a two-dimensional figure and only has two dimensions- length and width- while the cube is a three-dimensional figure with length, width, and height.
What is a Cube in Math?

In mathematical terms, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six equal squares, all right angles. Each of these squares is referred to as a ‘face,’ and all faces are congruent, meaning they have the same size and shape. This definition might sound complex, but in reality, cubes are part of our everyday life. Think of dice or a Rubik’s cube!
Anatomy of a Cube
To fully understand what a cube in mathematics is, it’s crucial to grasp its basic components: faces, edges, and vertices.
Faces of a Cube
A cube consists of six square faces, each identical to the others in terms of size and shape. These faces define the outer boundary of the cube and contribute to its symmetrical appearance.
Edges of a Cube
The edge of a cube is the line segment where two adjacent faces intersect. Since each face is a square with four edges, and there are six faces, a cube ends up with 12 edges overall. The edges form the framework that holds the cube together.
Vertices of a Cube
The vertex (or vertices for plural) of a cube is the point where any three edges meet. Given that a cube has 12 edges, it possesses eight vertices in total. These vertices act as the connecting points for the cube’s edges, creating the characteristic corners of the shape.
Properties of a Cube
Now that we’ve answered “How many edges does a cube have?”, “how many sides does a cube have?”, and “How many vertices does a cube have?”, let’s discuss some fundamental properties of a cube:
- All faces of a cube are identical squares.
- A cube has 12 equal edges.
- It features eight vertices.
- Each face of a cube is connected to four other faces.
- Each vertex of a cube is the meeting point of three faces and three edges.
- The angle between any two faces is 90°.
Cube Net

A cube net is a representation of a cube in the two-dimensional flat form which illustrates all six faces of the cube functionally laid out flat so that the net should be cut and folded into a three-dimensional cube. With the net between the cube faces, you can well see that there is a square face at each of the six edges, and that puts all together and makes the cube.
Formulas Related to a Cube
Mathematics deals with formulas, and when it comes to cubes, there are several important ones to know for calculating the surface area, volume, and length of a diagonal.
Surface Area of a Cube
There are two types of surface areas of a cube – Lateral Surface Area (LSA) and Total Surface Area (TSA)
Lateral Surface Area of a Cube
The lateral area of a cube is the sum of areas of all side faces of the cube. There are 4 side faces so the sum of areas of all 4 side faces of a cube is its lateral area. The lateral area of a cube is also known as its lateral surface area (LSA), and it is measured in square units.
Lateral Surface Area of a Cube = 4 × (side)2, where a is the length of the side of a cube
Total Surface Area of a Cube
The total surface area of the cube is the sum of the area of the base and the area of the vertical surfaces of the cube. Since all the faces of the cube are made up of squares of the same dimensions, the total surface area of the cube will be the surface area of one face added six times to itself. It is measured as the “number of square units” (square centimeters, square inches, square feet, etc.). Therefore, the formula to find the surface area of a cube is:
Total Surface Area (TSA) of a Cube = 6a2
Volume of a Cube
The volume of a box is the space that the box itself occupies. The volume of a cube form can be obtained through the process of cubing the side length of the cube. Determining the volume of a cube requires a formula depending on the measurements or the parameter of the cube. The units used are cubic centimeters or millimeters, depending on what you are working with. The formula to find the volume of the cube is:
The volume of a cube = a³
Diagonal of a Cube
The diagonal of a cube is the line connecting two opposite corners of the cube. You can find the length of this diagonal using specific formulas for the cube’s face and main diagonals. Each face diagonal serves as the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle on the cube’s square faces. Since there are six faces, you end up with twelve face diagonals in total. Additionally, there are four main diagonals running through the cube’s interior and connecting opposite corners.
To calculate the lengths:

The face diagonal length is given by √2 times the length of a side (a).
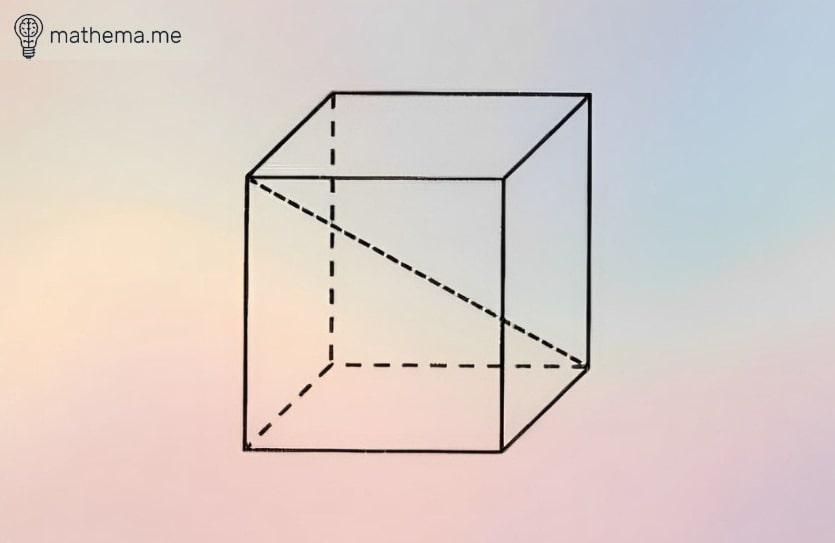
The main diagonal length is √3 times the length of a side (a).
Real-life Examples of Cubes
Cubes are not just mathematical concepts; they have practical applications in our daily lives. Here are a few examples:
- Dice: Each side of a die is a perfect square, making it a cube.
- Ice Cubes: These are typically cube-shaped to fit efficiently in a glass or bottle.
- Rubik’s Cube: This puzzle game is a perfect example of a cube.
Conclusion
The cube is a fascinating and fundamental concept in mathematics. Understanding this three-dimensional shape can enhance your child’s comprehension of space, symmetry, and geometry. For more engaging and interactive learning about the cube and other mathematical concepts, check out Mathema. This platform makes learning math fun and accessible for learners of all ages.
FAQs on Cube
1: What is a cube in math?
A cube in mathematics is a three-dimensional geometric figure with six congruent square faces, 12 equal edges, and eight vertices.
2: How many edges does a cube have?
A cube has 12 edges.
3: How many sides does a cube have?
A cube has six faces or sides.
4: How many vertices does a cube have?
A cube has eight vertices.
5: What real-life objects are shaped like cubes?
Examples of real-life cubes include dice, ice cubes, and Rubik’s cubes.



